


Next: Introduction and Overview
Up: Declared-Strategy Voting: An Instrument
Previous: Declared-Strategy Voting: An Instrument
- amendment procedure
- A voting procedure that pairs a proposal
under consideration with the status quo. If a variation on the
proposal is introduced it is paired with the proposal and voted on
as an amendment prior to the final vote. If the amendment succeeds,
then the amended proposal is eventually paired with the status
quo in the final vote.
- approval voting
- A voting procedure in which voters may vote
for (approve of) as many of the alternatives as they wish.
- Borda count
- A voting procedure in which each voter forms a
preference ranking for all alternatives. Given n alternatives,
each voter casts n votes for his or her most preferred
alternative, n-1 votes for his or her second most preferred
alternative, etc. The alternative that receives the most votes wins.
- cardinal utility
- A preference expressed in terms of intensity
on a finite scale.
- Condorcet criterion
- Holds for a voting system if it selects
the Condorcet winner whenever one exists.
- Condorcet efficiency
- Percentage of elections in which the
Condorcet winner is selected (assuming there is a Condorcet winner).
- Condorcet winner
- An alternative that beats or ties all others
in a series of pairwise contests.
- consistency
- Holds for a voting system if when the electorate is
divided arbitrarily into two parts and separate elections in each
part result in the same alternative being selected, an election of
the entire electorate also selects that alternative.
- coordinated macromanipulation
- Manipulation by coalitions.
- cumulative vote
- A semiproportional voting system in which each
voter is alloted a number of votes equal to the number of candidates
to be elected. The voters may give one vote each to that number of
candidates or accumulate their votes, allocating two or more to one
candidate.
- declared-strategy voting
- (DSV) A novel group decision-making
procedure in which preference is specified using voting
strategies.
- deterministic
- Holds for a voting system if it always produces
an election winner.
- effectiveness
- The power of a ballot to influence the election
outcome.
- expressiveness
- The extent to which a voting system allows
voters to voice their honest opinions without sacrificing the power
of their votes.
- independence from irrelevant alternatives
- Holds for a voting
system if it always produces the same results given the same profile
of ordinal preferences.
- insincere vote
- A vote that is not sincere.
- limited vote
- A semiproportional representation system similar
to plurality voting, except voters are limited to casting a number of
votes that is less than the number of candidates to be elected.
- list proportional representation
- (list PR) A proportional
representation system in which political parties prepare lists that
include as many candidates as there are seats to be filled. The
voters select the list for the party they support and deposit it in
their ballot envelopes. After the votes are counted and the seats
are allocated, each party selects from the top of its list the
number of candidates corresponding to the number of seats won. Some
variations on this procedure allow voters the option of crossing out
candidates or selecting particular candidates from a party list.
- majoritarian voting method
- A voting method that selects a
winner based on pairwise comparisons between alternatives.
- majority rule
- A voting system in which the alternative
receiving more than half the votes wins.
- manipulability
- Holds for a voting system in which voters may
sometimes obtain a more preferred outcome by casting ballots not
reflective of their true preferences.
- micromanipulation
- Manipulation by individuals.
- monotonicity
- Holds for a voting system if when a voter raises
the valuation for a winning alternative it remains a winning
alternative, and when a voter lowers the valuation for a losing
alternative it remains a losing alternative.
- multi-stage voting method
- A voting procedure that uses either
different choice functions at different stages of the procedure, or
one choice function iteratively on diminishing sets of alternatives.
- neutrality
- Holds for a voting system if the system does not favor any
alternative.
- non-dictatorial
- Holds for a voting system if the election outcome is
not determined entirely by a single individual.
- NP-hard
- Cannot be solved in polynomial time.
- ordinal utility
- A preference expressed in terms of relative
position in a list of alternatives ordered according to preference.
- Pareto optimality
- Holds for a voting system if when every
voter prefers alternative x to alternative y, alternative y is
not selected.
- pivot probability
- The probability that a voter will be
decisive in creating or breaking a first-place tie between two
candidates (or for elections that select M alternatives, the
probability that the voter will be decisive in creating or breaking
an
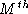 -place tie).
-place tie).
- plurality voting
- A voting procedure in which each voter votes
for his or her single most preferred alternative (or when n
alternatives are to be selected, voters vote for their n most
preferred alternatives). The alternative that receives the most
votes wins.
- positional voting method
- A voting method that selects a winner
based on information about individuals' preference orderings.
- proportional representation system
- (PR) A voting system that
promotes close correspondence between the proportion of supporters
of each party (or other interest group) in the electorate and the
proportion of seats held by each party in a governing body.
- rational
- Holds for voters that take actions they believe are
most likely to lead their preferred outcome -- regardless of
whether it is reasonable for them to prefer that outcome.
- runoff election procedure
- A two-stage voting procedure in
which the alternatives are first considered together, and then if no
alternative receives the majority of votes, a majority rule election
is held between the two alternatives receiving the largest numbers
of votes.
- semiproportional voting system
- A voting system with similar
properties as the proportional voting systems, but resulting in
somewhat less proportional representation.
- sincere vote
- A vote such that for any two alternatives
under consideration, the voter has given greater or equal weight to
the more preferred of those alternatives.
- single-stage voting method
- A voting method that selects a
winner in a single round of vote tabulation.
- single non-transferable vote
- (SNTV) A special case of the
limited vote in which voters may specify only a single candidate on
their ballots, regardless of how many seats are to be filled.
- single transferable vote
- (STV) A voting procedure in which
voters submit a preference raking over all the candidates. Any
candidate that receives more than a certain number of first-place
votes is elected. If the elected candidates receive more votes than
necessary for election, their excess votes are distributed to the
other candidates in accordance with the second-choice preferences of
the voters. Once again, any candidate that receives more than a
certain number of votes is elected and the redistribution procedure
continues. If the redistribution procedures reaches a point where
there are no more votes to be redistributed and there are still more
elected positions to be filled, the candidate with the least votes
is eliminated and the votes for that candidate are redistributed.
- sophisticated vote
- A vote determined to be optimal through
game theoretic analysis, which takes into account the likely
strategies of the other voters; a type of strategic vote.
- stability
- Producing the same outcome from a given set of
ballots each time it is counted.
- strategic vote
- A vote such that for any two alternatives
under consideration, the voter has given greater or equal weight to
the more preferred of those alternatives.
- utilitarian voting method
- A voting method that requires voters
to assign utility values to each alternative. These utilities
are aggregated to determine the election outcome.
- utility
- A preference; a measure of personal value or satisfaction.
- voting strategy
- A plan made prior to an election that
prescribes the course of action a voter should take given any
contingency that can arise.



Next: Introduction and Overview
Up: Declared-Strategy Voting: An Instrument
Previous: Declared-Strategy Voting: An Instrument
lorrie@acm.org